Multi-Agent Learning学习与实践
Multi-Agent Learning学习与实践
Multi-Agent Actor-Critic for Mixed Cooperative-Competitive Environments
该篇论文提出了MADDPG
Successfully scaling RL to environments with multiple agents is crucial to building artificially intelligent systems that can productively interact with humans and each other.
Unfortunately, traditional reinforcement learning approaches such as Q-Learning or policy gradient are poorly suited to multi-agent environments.
就是说,multi-agent learning的环境可能在变化。而传统的Q-learning策略依赖于过去的学习经验来使学习过程稳定。
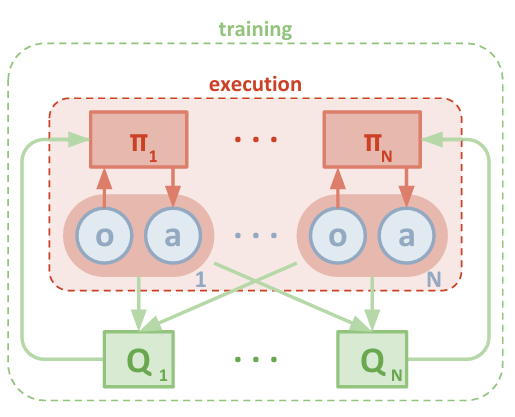
采用的学习策略是centralized training with decentralized execution。
执行过程中,每个agent只使用local information(自己的观测)。
multi-agent decentralized actor, centralized critic方法示意图
一个包含$N$个agent的场景,每个agent产生policy的网络定义为$\pmb{\theta}={\theta_1,…,\theta_N}$,产生的policy定义为$\pmb{\pi}={\pi_1,…,\pi_N}$
这里其实涉及到强化学习的两种方式:Policy-based learning(Policy gradient)以及Value-based learning(Q learning)。而Actor-Critic合并了这两种方式。
Actor 基于概率选行为, Critic 基于 Actor 的行为评判行为的得分, Actor 根据 Critic 的评分修改选行为的概率。
Actor Critic优点:可以进行单步更新, 相较于传统的PG回合更新要快.
Actor(玩家):为了玩转这个游戏得到尽量高的reward,需要一个策略:输入state,输出action,即上面的第2步。(可以用神经网络来近似这个函数。剩下的任务就是如何训练神经网络,得更高的reward。这个网络就被称为actor)
Critic(评委):因为actor是基于策略policy的所以需要critic来计算出对应actor的value来反馈给actor,告诉他表现得好不好。所以就要使用到之前的Q值。(当然这个Q-function所以也可以用神经网络来近似。这个网络被称为critic。
更形象的形容,Actor是舞台上的舞者,Critic是台下的评委。Actor在台上跳舞,一开始舞姿并不好看,Critic根据Actor的舞姿打分。Actor根据Critic给出的分数去学习。如果Critic给出的分数高,那么Actor会调整这个动作的输出概率。相反,如果Critic给的分数低,那么就减少这个动作的输出概率。
Extended Python MARL framework - EPyMARL
https://github.com/uoe-agents/epymarl?tab=readme-ov-file
Benchmarking Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Cooperative Tasks
这篇文章为Multi-Agent Learning提供了一个公用的benchmark